In logistics, pallets play a big role in moving goods smoothly across the globe. There are markings on pallets to inform the people about the pallet type and more. However, the symbols and codes on them can be confusing. Knowing what these markings mean isn’t just for experts it’s also useful for anyone shipping, receiving, or even reusing pallets for personal projects.
In this guide, we’ll explain these markings to help you understand them better and make smarter decisions for your shipments.
By Lucas Bonavita
December 13, 2024 • 15 min read

Pallet markings serve as a universal language, conveying crucial information about the pallet’s origin, treatment, and suitability for specific uses (mostly shipping purposes). They ensure compliance with international regulations, prevent the spread of pests and diseases, and indicate ownership.
For businesses, these markings are vital for smooth customs clearance and maintaining supply chain integrity.
For individuals, especially DIY enthusiasts, knowing these symbols can safeguard against using chemically treated or unsafe pallets.
Pallets can feature a variety of markings, each serving a unique purpose. The primary types include:

The International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures No. 15 (ISPM 15) is a guideline developed to prevent the international transport and spread of diseases and insects that could negatively affect plants or ecosystems. Pallets used in international shipping must comply with these standards.
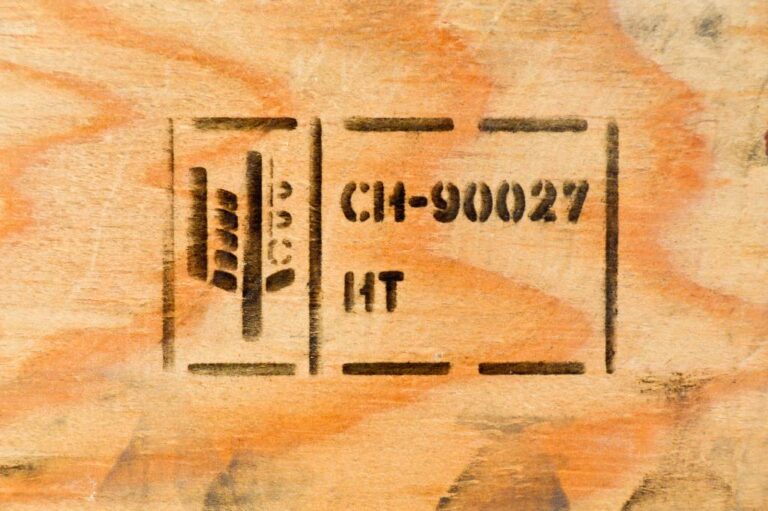
At the heart of ISPM 15 compliance is the IPPC (International Plant Protection Convention) symbol, depicted as a stylized wheat ear within a rectangle.
This mark certifies that the pallet meets international phytosanitary standards and is safe for cross-border movement.
Adjacent to the IPPC symbol, you’ll find a two-letter ISO country code indicating where the pallet was treated. For instance, “DE” for Germany or “FR” for France. Click here to check the ISO codes.
These codes reveal the method used to treat the wood, ensuring it’s free from pests.
These markings provide traceability and indicate ownership.
Company Logo
A company’s logo may be stamped on the pallet, especially if it’s part of a pallet pooling system. This denotes ownership and should be respected to avoid legal issues.
Serial Numbers or Batch Codes
Serial numbers help in tracking and quality control, identifying when and where the pallet was produced.
These symbols or numbers specify the maximum load the pallet can carry. Adhering to these limits is crucial for safety and maintaining the integrity of goods during transport.
A unique identifier is assigned to the manufacturer or treatment provider by the national plant protection organization, ensuring accountability.
This number indicates which authority certified the pallet’s compliance, adding an extra layer of trust.
Grades classify pallets based on their condition:
Grade A: New or like-new condition.
Grade B: Used but in good condition with minor repairs.
Grade C: Heavily used, may require significant repairs.
Modern pallets may feature QR codes or RFID tags, enabling digital tracking and providing instant access to detailed information about the pallet’s history and specifications.
Symbols indicating that a pallet is made from sustainable sources or recycled materials align with eco-friendly practices.
Quicargo enhances these efforts by operating a 100% digital platform, enabling faster communication and greener operations. By optimizing empty truck space, Quicargo minimizes carbon footprints, contributing to more sustainable logistics solutions.
Certain industries require specific pallet standards, such as those for pharmaceuticals or food, which may have additional markings to indicate compliance.
The EPAL mark signifies that the pallet meets the stringent standards set by the European Pallet Association. EPAL pallets are widely used across Europe for their reliability and quality. Learn more here.

The PRL (Pallet Return Logistics) stamp indicates a pallet is part of a rental or pooling system, designed for efficient return and reuse within specific supply chains.
Repaired pallets often have a nail or staple with a marking to indicate they’ve been refurbished according to industry standards, ensuring they remain safe and functional.
Understanding the distinction between HT and MB is crucial. Heat treatment is a physical process using high temperatures to eliminate pests without chemicals, making it environmentally friendly and safe for handling.
Methyl bromide fumigation involves a potent pesticide harmful to humans and the ozone layer.
Due to these risks, MB-treated pallets are prohibited in many countries. Always opt for HT-marked pallets for safety and compliance.
Colored pallets are not just aesthetically different; they often signify ownership or specific uses within supply chains
Blue pallets are typically owned by CHEP, a global supply chain company. They’re used in pooling systems and remain the property of CHEP.
Red pallets belong to LPR (La Palette Rouge), prominent in the European market. They’re part of a rental system and are maintained to high standards.
Yellow pallets may indicate ownership by certain companies or be used within specific industries. Always check for additional markings to determine their purpose.
Green pallets often denote eco-friendly materials or practices, such as using recycled wood or sustainable manufacturing processes.
Black pallets are usually designated for heavy-duty industrial use, built to carry heavier loads and withstand harsher conditions.
Unmarked pallets are generally used for domestic transport and may not comply with international standards. They may not have undergone any treatment, posing potential risks for pest infestation or chemical exposure. For international shipping or projects involving direct human contact, it’s advisable to avoid unmarked pallets.
Markings should be durable, clear, and easy to read. They’re typically applied using indelible ink, branding, or stamping methods. Legibility ensures quick identification and compliance during inspections, reducing delays and misunderstandings in the supply chain.
Examine the pallet for the ISPM 15 stamp and look for the treatment code, such as “HT” or “MB”. The absence of these markings likely means the pallet hasn’t been treated according to international standards, making it unsuitable for international shipping and potentially unsafe for reuse.
Unmarked pallets are unlikely to have been treated under ISPM 15 guidelines. They might be safe for local use but are not recommended for applications where treatment is essential, such as international shipping or furniture making.
Euro pallets, especially those marked with EPAL, are not chemically treated. They undergo heat treatment, aligning with European regulations that prioritize safety and environmental considerations.
Pallet organizations play a crucial role in standardizing and regulating pallet production and usage across industries. They ensure compliance with safety, quality, and environmental standards, supporting efficient and sustainable global trade logistics.
Navigating pallet regulations can be complex, but shipping doesn’t have to be. Learn more about pallet shipping with Quicargo, or start shipping today. Our expertise ensures your goods move safely and efficiently across Europe.
Also read: Shipping Pallets
Ready to join Quicargo? Your freightforwarder for Europe shipments.
Start shipping
✓ Ship to 29 countries ✓ Save 30% in Costs ✓ Save time






Ship with Quicargo. Save costs, and time .
Join Quicargo
You have already subscribed.
Join 12.000+ subscribers.
We're commited to your privacy. You may unsubscribe at any time.
